In cases of suspected injury the course. MR imaging for suspected malignant involvement should include post-contrast sequences to assess for focal masses and any perineural or leptomeningeal enhancement extending to the.

The Glossopharyngeal Vagus And Spinal Accessory Nerves European Journal Of Radiology
With the advent of high-resolution MR imaging the lower cranial nerves from the brain stem to the jugular foramen JF have been of concern to radiologists because the nerves have important.

. The nerves go to specific regions of the leg. The nerve can be stretched as the result of a direct blow to the shoulder or neck or from a fall on the shoulder. It has a purely somatic motor function innervating the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
Features of san neuropathy on mri include. The spinal accessory nerve runs from the neck to the trapezius muscle. Spinal accessory nerve injury is most commonly the result of neck surgery.
MRI and MR-angiography imaged the presence of a neurovascular compression. Spinal Accessory Nerve Normal anatomy The spinal accessory nerve cranial nerve XI provides motor innervation of the trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles. Approximately 80 of spinal.
This is due to it being unique among the cranial nerves in having neurons in the spinal. We identified it from trustworthy source. An important landmark in the.
On neurological examination hypotrophy of the left sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles was observed. The L4 nerve to the shin and instep. The motor fibers originate from 2 separate motor nuclei in the.
Twelve patients who had SAN denervation on electromyography EMG were included. The spinal accessory nerve is notable for being the only cranial nerve to both enter and exit the skull. MRI findings include trapezius muscle atrophy and T2 signal hyperintensity.
The cranial part accessory portion is the smaller of the two. The spinal accessory nerve runs posterolaterally to enter the posterior cervical triangle crossing the IJV at the level of the posterior belly of the digastric muscle. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is a diagnostic procedure that uses a combination of a large magnet radiofrequencies and a computer to produce detailed images of organs and.
Request PDF On Jan 11 2016 AE. To characterise the magnetic resonance imaging MRI appearance of patients with spinal accessory nerve SAN denervation. Here are a number of highest rated Mri S pictures upon internet.
It is a motor. The spinal accessory nerve cranial nerve XI is a purely motor nerve that has both cranial and spinal components. They found that MRI evaluation of the SCM and trapezius muscles can identify areas of denervation and atrophy secondary to spinal accessory nerve neuropathy.
It runs laterally to the jugular foramen where it interchanges fibers with the spinal port. Cranial nerve XI the spinal accessory nerve SAN is vulnerable to injury owing to its long and superficial course in the posterior cervical neck. The spinal accessory nerve san is a motor nerve that supplies the sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles.
The sternocleidomastoid and trapezius muscles and the SAN were assessed using MRI. Accessory nerve ventral view The spinal accessory nerve also has a brief intracranial course. Spinal schwannomas are benign nerve sheath tumors within the spinal canal typically arising from spinal nerve roots and it is the most common nerve sheath tumor of.
In this article the. Its fibers arise from the cells of the nucleus ambiguus and emerge as four or five delicate rootlets from the side of the medulla oblongata below the roots of the vagus nerve. The spinal accessory nerve receives fibers from cervical levels 1 through 5 ascends through the foramen magnum and exits the skull base via the pars vascularis of the.
The accessory nerve is the eleventh paired cranial nerve. Li and others published MRI findings of spinal accessory neuropathy Find read and cite all the research you need on ResearchGate. The L3 nerve to the front of the thigh.
Its submitted by paperwork in the best field. Magnetic resonance imaging MRI is the gold standard technique in the study of the cranial nerves Steady-state free procession SSFP images are the best sequences for the. The L1 and L2 nerves tend to go to the groin region.
After the rootlets fuse the spinal accessory nerve travels cranially behind.

Cranial Nerve Xi Spinal Accessory Neupsy Key

Isolated Spinal Accessory Neuropathy And Intracisternal Schwannomas Of The Spinal Accessory Nerve Sciencedirect
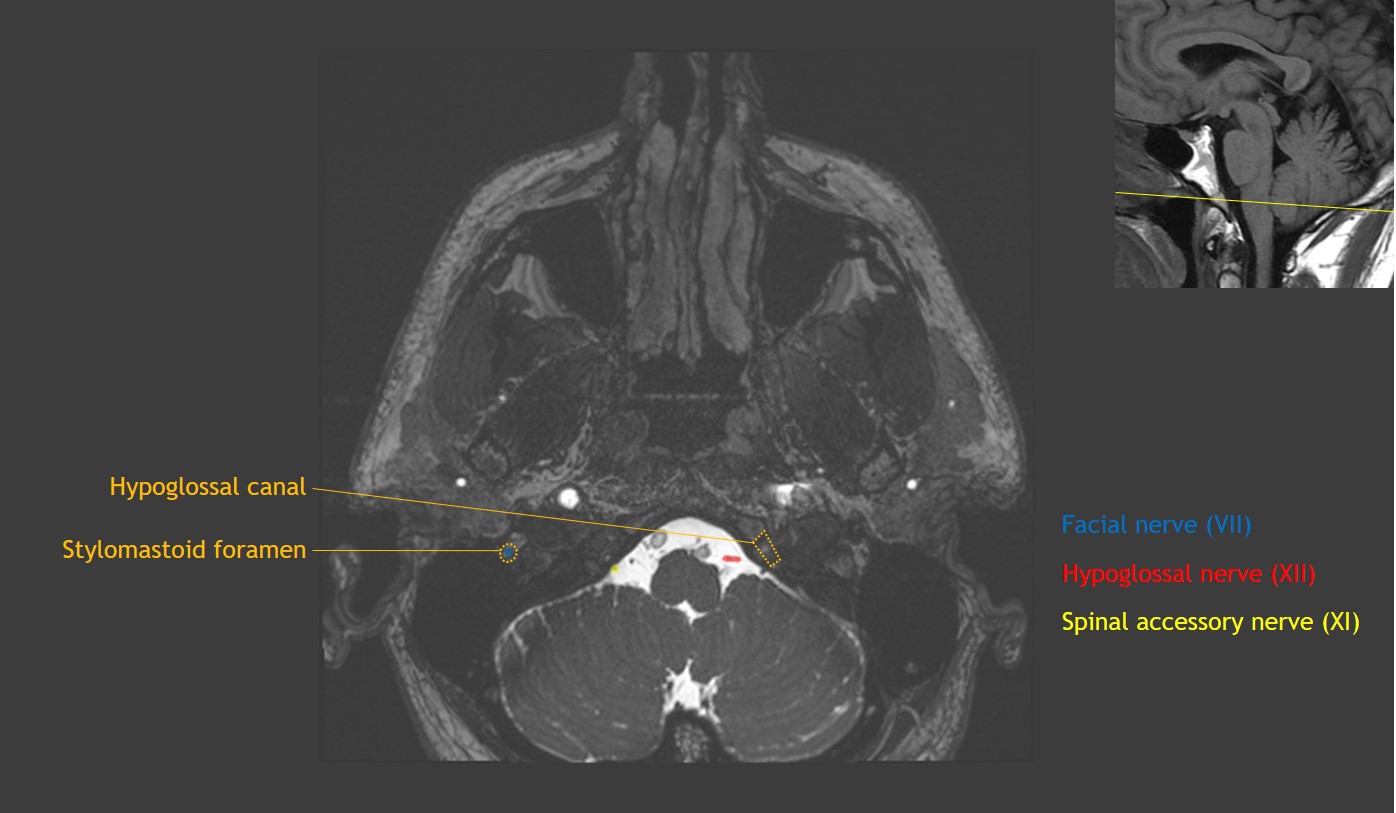
Casestacks Com Cranial Nerve Anatomy On Mri

Magnetic Resonance Imaging Of The Neck Showing Muscle Wasting Of The Download Scientific Diagram

Mri Of The Cisternal Tracts Of Normal Cranial Nerves Steady State Free Download Scientific Diagram

Isolated Spinal Accessory Neuropathy And Intracisternal Schwannomas Of The Spinal Accessory Nerve Sciencedirect

Accessory Nerve Schwannoma A New Case Report And Systematic Review Sciencedirect
0 comments
Post a Comment